
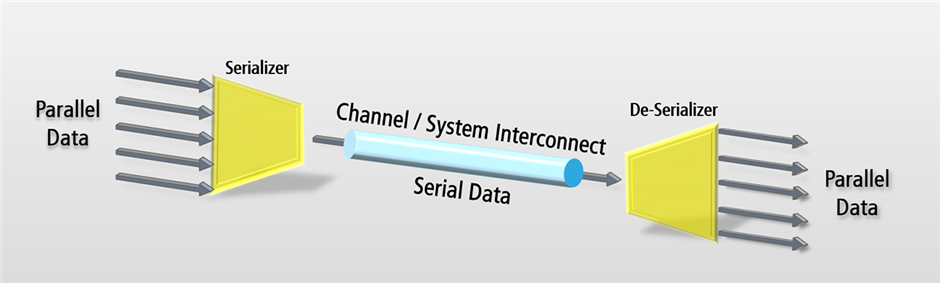
SATA host adapters and devices communicate via a high-speed serial cable over two pairs of conductors. However, the ATA specifications simply use the name "AT Attachment", to avoid possible trademark issues with IBM. "AT" was IBM's abbreviation for "Advanced Technology" thus, many companies and organizations indicate SATA is an abbreviation of "Serial Advanced Technology Attachment".

The IBM AT's controller interface became a de facto industry interface for the inclusion of hard disks. The "AT Attachment" (ATA) name originated after the 1984 release of the IBM Personal Computer AT, more commonly known as the IBM AT. The remainder of this article strives to use the SATA-IO terminology and specifications.īefore SATA's introduction in 2000, PATA was simply known as ATA. As with many other industry compatibility standards, the SATA content ownership is transferred to other industry bodies: primarily INCITS T13 and an INCITS T10 subcommittee ( SCSI), a subgroup of T10 responsible for Serial Attached SCSI (SAS). The SATA-IO group collaboratively creates, reviews, ratifies, and publishes the interoperability specifications, the test cases and plugfests. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO). Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then promulgated by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA ( SATA, abbreviated from Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. ( Learn how and when to remove this template message)
Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
